Data capacity
Data capacity is used to express the capacity of a storage device such as a memory stick, hard drive or optical disc. Storage capacities are discussed here.
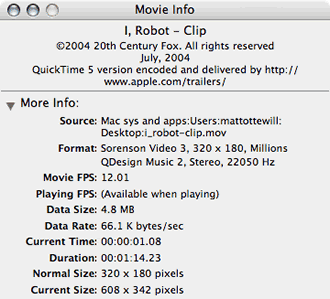
The info dialogue box showing the compression codecs, settings,
data rate/size etc for a Hollywood film QuickTime video clip trailer.
Data size
"Data size" is the total size of a given file. In the case of audio and video this will be the file's data rate multiplied by the file's duration in seconds.
You will be concerned with data size for the following reasons ...
- Because all storage devices have finite capacity you will need to ensure that your data will fit on your chosen storage media.
- If an end-user must download a complete file before viewing and time is an issue. How long will your end-user be willing to wait?
- If your data files are so large that they place unreasonable demands on the free application RAM of your end-user's system.
Data size is expressed in Bytes, KiloBytes, MegaBytes, GigaBytes etc. A website image may typically be several tens of kilobytes (30Kb), audio will be measured in Mb's and video in tens or hundreds of Mb's or even Gb's.
Data rate (or Bit rate)
"Data rate" is used to measure ...
- The average amount of data per second that a file (video, audio etc) contains.
- The maximum speed of a connection technology such as USB, Firewire or an internet connection, also known as Bandwidth.
- The speed with which data can be transferred from a storage device to RAM (normally referred to as "sustained data transfer rate")
Note that data rate is usually expressed in bits, thus 256Kbps = 256 Kilo bits per second (ie 8 times slower than KiloBytes per second).
Data rate for internet audio and video
Clearly audio/video data will arrive in RAM ready to be played faster from an internal hard disc drive than a 56Kbps internet connection. When creating media for web sites it is first essential to profile your end-users and determine their average connection speed. The data rate of the media file will need to be close to or below the network speed if the file is too play quickly and without interruption.
Bandwidth
For a more in-depth discussion of Bandwidth click here.
