To create network (internet etc) friendly audio file sizes
To reduce the size of video files by compressing the soundtrack audio
To compress audio for DVD authoring
NOTE: If you have not already read the article on Digital Audio File Formats you should do so before reading this page.
What is a codec?
A codec is a piece of software, sometimes called an algorithm, which is used to compress a media file (reduce its size) and then later decompress it before it is played. This process is useful for 2 primary reasons ...
- To allow more data to be stored on a given storage device (such as a digital video camcorder hard drive or memory card).
- To increase the speed of transmission across a network (such as the internet).
The term "codec" is usually used in reference to audio and video media files, but still image compression methodologies, such as jpeg, can also be called codecs. A codec may be lossy (cause some deterioration in quality) or lossless.
A "hard codec" is integrated into the electronics of a hardware processor/device such as a camcorder, MP3 player or video capture card. A "soft(ware) codec" is installed onto a system and runs on the systems CPU. QuickTime mostly comprises a collection of soft codecs which run on a PCs CPU and can be used by any application installed on the system, such as a web browser or video editing application.
Examples codecs are ...
- .jpg (images)
- .mp3 (audio)
- .mp4 (video)
Compressing video soundtracks
Compressing audio/music for the web
MP3
As you are no doubt aware, MP3 is the current dominant file format for the web. Its popularity makes it the best choice and almost guarantees compatibility with all internet end-user systems.
Flac
You may also be interested in Flac (Free Lossless Audio Codec) which offers lossless high quality compression. However, whilst almost all end-users will have no trouble listening to MP3 files, many will not have the necessary device / software to replay Flac files. More at flac.sourceforge.net
MP3 compression programs
Many people use iTunes to convert uncompressed CD quality audio into MP3 files but almost all audio editing software will allow you to export to MP3. Programs include ...
- iTunes
- Cubase
- Logic
- Performer
- Sound Forge
- Peak
- Audacity
- etc
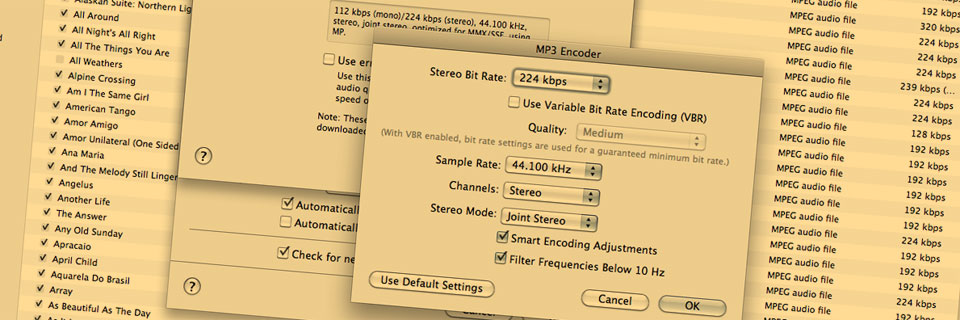
iTunes MP3 encoder settings.
MP3 parameters (settings) to alter
When creating MP3 file you can experiment with the following settings ...
- Data Rate This will vary the "strength" of compression. How this achieved depends on the compression codec and it is rare to have access to more than just an overall bit rate (kilo bits per second) control.
- Variable bit rate This constantly alters the bit rate to achieve the best file size to quality ratio for the material.
- Sample rate Use 44.1kHz if you can. 32kHz is acceptable and you will notice a loss of quality at 20.050kKHz.
- Bit-depth Use 16-bit if you can. 12-bit is acceptable.
- Channels I use mono for previews and stereo for everything else
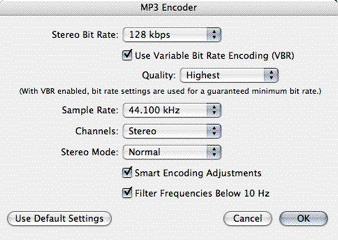
Suggested MP3 parameter settings
Experiment but here are a few suggestions ...
- Previews = 96kbps, 32kHz, 12bit, mono, variable bit rate on/medium quality
- Standard quality = 128kbps, 44.1kHz, 16bit, stereo, variable bit rate on/medium quality. Most internet MP3 file are encoded with these settings
- High quality = 192 - 224kbps, 44.1kHz, 16bit, stereo, variable bit rate on/high quality
AAC compression
if you choose the AAC encoder in iTunes it chooses settings automatically for you. Try it out. If anyone knows more about this codec and alternative ways to encode files with it, please us know.