Now, re-visualise/imagine your bike a different colour. Done it? You've just sent data with some processing instructions down the system bus from your RAM to your CPU (Central Processing Unit) which made the calculation/adjustment of colour to the data before putting it back in your RAM.
Now, see if you can remember tomorrow, what colour you changed your bike to. If you can, you will have successfully stored it back on your hard disc drive. Data in RAM must be stored onto the hard drive because when you start thinking about something else (quit a program and load another) or go to sleep (shut down your computer) then the contents of RAM are lost.
Learning is the process of getting new data in our RAM stored on our hard drives. Computers can do it instantly, humans usually take a little longer.
![]() This diagram (Computer system diagram) may help you understand these processes.
This diagram (Computer system diagram) may help you understand these processes.
6 different physical states of digital signals
Units of storage & memory
Click here to find out about Bits, Bytes, KiloBytes etc before you continue reading this page.
Hardware components
Modern computers systems comprise a linked group of hardware devices. These are:
- Input devices for entering commands and inputting data.
- Output devices for outputting finished work
- Processing devices for carrying out the "thinking" and processing tasks.
- Memory devices.
- Storage devices for saving, loading and storing the Operating System, Programs and Data.
- Interconnection ports/sockets for connecting to other equipment/systems
- Expansion cards for adding additional processing functionality to a computer.
- Motherboard to which all of the above are attached. This routes all the digital signals from one device to another.
- Case and power supply
Input devices
- Keyboard & mouse
- MIDI interface
- Soundcard
- Modem
- Scanner
- etc
Output devices
- Monitor screen
- MIDI interface
- Soundcard
- Modem
- Printer
- etc
Processing devices
There are several types of processing chip (or device). The 2 most important general categories are ...
1. CPU (Central Processing Unit)
The calculating brain of the computer where all the logical calculating processes are carried out. This carries out all the general calculating processes. Examples include ...
- Intel Pentium.
- Athlon, AMD.
- IBM G5

2. DSP (Digital Signal Processors)
DSP chips are usually designed to carry out specific tasks and are often located on Expansion Cards (see later). Typical examples include ...
- Soundcard's and audio DSP cards. DSP chips carry out tasks such as synthesis, mixing and effects processing, thereby taking the load off the CPU and giving additional power.
- Graphics cards. DSP chips provide extra power to help improve the performance of games, speed up 3D rendering and video editing.
Memory devices
- RAM (Random Access Memory). The working memory (short term) of the system which holds the Operating System, Programs and Data whilst the computer is on. It empties when the computer is turned off. Much more expensive than hard disc per Mb. Typical PC installed RAM (2004) is between 500Mb and 1Gb.
- Flash RAM. A type of RAM which holds its contents even when the power is off. Much more expensive than RAM.
- ROM (Read Only Memory). ROM memory is generally used to permanently store parts of the Operating System. A synthesiser holds its Operating System in ROM memory. It cannot be emptied even when the computer is off.

Storage devices
3 primary types ...
1. Magnetic drives such as ...
- Hard disc drives read and write data faster than any computer storage device (floppy, optical, tape etc). They have large storage capacities but data must be backed up to a second hard drive or removable optical discs when the disc becomes full or for safety reasons. The Operating System, Programs and Data will be stored and loaded from the hard drive. Computers always have at least 1 internal drive, but others may be installed internally or connected externally using US, SCSI or FireWire cables.Read all about using hard drives by clicking here.
- Floppy disk drives (capacity 1.4Mb). Yesterdays technology, well on the way out. Anything small enough to fit on a floppy can be emailed between computers.
Formatting All new magnetic media (Floppy disks, hard drives, removable cartridges) need to be formatted before use. Formatting put a filing system onto the disk and prepares it to receive data. Every operating system uses a different filing system which often makes media incompatible between platforms. Read more about hard drives and formatting here.
2. Optical drives such as ...
- CD-ROM / CD-R (recordable) drives (capacity 650Mb)
- DVD-ROM / DVD-R (recordable) drives (capacity 4.2Gb)
On the surface of a commercially pressed /manufactured optical disc (CD / DVD ROM) a pit is essentially an indentation or hole (pressed from a glass master) and a land is an area unaffected. A reading laser shines light onto the surface of the disc. The light takes longer to reflect from a pit than a land. This discrepancy in the wavelength of the reflected light allows the laser to produce 1s and 0s.

CD-R/RW and DVD-R/RW work differently by using a laser to change the colour of a light sensitive surface making them susceptible to damage from direct light sources such as sunlight.
3. Solid State Drives
Solid state drives are essentially like large Flash RAM storage devices. Typical current capacities are between 256 and 500Gb. These drives are compact,energy efficient, fast and useful as system drives, and sound library drives for DAW systems, but their high cost and low capacities compared to magnetic hard drive storage means they are still not widely used yet (Jan 2015) except in laptops. Also, there are some issues regarding their longevity and decreasing efficiency over time. Nethertheless their speed means a system can boot, and files can load and save, in a fraction of the time taken by magnetic drives.
Click here for storage capacities of different devices and media
Click here for help on backing up to optical discs
Interconnection
Additional hardware (printers, scanners, cameras etc) can be connected to a computer using one of 4 primary types of connection. Here are the the current most common ...
| Interconnection type | Connector | Symbol | Speed | Used for |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Universal Serial Bus / USB 1 | Several types including ...  |
Up to 12 MBits/sec | Printers, scanners, external hard drives, memory sticks, MIDI interfaces, digital cameras etc | |
| Universal Serial Bus / USB 2 | As USB 1 | As USB 1 | Up to 60Mb/sec | As USB 1. Used for wide range of devices including digital SLRs and audio interfaces |
| Universal Serial Bus / USB 3.0 (SuperSpeed USB) | Uses an optical connector |  |
Up to 625Mb/sec | Used for wide range of devices including digital SLRs and audio interfaces |
| USB 3.1 | Up to 1,250Mb/sec | |||
| Firewire 400 |  |
Up to 49Mb/sec | High end scanners, printers, fast AV external hard drives, semi-professional audio interfaces, DV camcorders etc | |
| Firewire 800 |  |
As Firewire 400 | Up to 98Mb/sec | High end scanners, printers, fast AV external hard drives, semi-professional audio interfaces, HD camcorders etc |
| Ethernet |  |
- | Gigabit = 125Mb/sec Wifi/IEEE 802.11n = 75Mb/sec 10BaseT = 10MBits/sec 100BaseT = 100MBits/sec 1000BaseT = 1000MBits/sec |
Multiple general uses such as ... Networking (computers, servers, hubs, switches etc), connecting network devices such as printers, audio system networking etc and professional audio interfaces |
| eSATA |  |
- |
300Mb/sec and 600Mb/sec | External hard drives |
| Thuderbolt 1 |  |
 |
Two channel at 1.25Gb/sec | Potentially anything |
| Thunderbolt 2 | 2.5Gb/sec (single channel) |
Expansion cards
All desktop computers include several expansion slots on the motherboard to which additional processing cards can be fitted in order to extend the functionality of a computer.

The current standard format for these cards is PCI and AGP for hi-end graphics cards. A typical desktop computer will have 4 to 6 expansion slots.
Typical expansion cards include ...
- Soundcard
- Graphics card (for the monitor)
- Ethernet networking card
- Additional ports ... FireWire or USB
- 3D gaming accelerator cards
- Video capture (in/out) digitising cards which may also include dedicated DV codec chips
- DVD decoder cards (MEPG-2) to allow a computer to replay DVD video discs
Motherboard
The motherboard is the large printed circuit board to which are attached all the other hardware device. Some of these devices are connected via cables, others plug into "expansion slots", whilst others are soldered or fitted to the board directly.
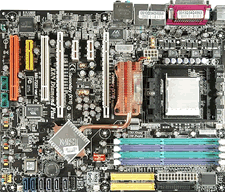
| Connections to motherboard | ||
|---|---|---|
| Via cables | Via expansion slots | Directly |
| Hard drives | Soundcard's | CPU |
| Optical drives | Graphics cards | |
| Power supply | RAM memory cards | |
Software components
Software may be divided into three categories. Click here to read about them.
Software copyright protection
Click here for an article on anti-piracy methodologies.

